green ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica)
Oleaceae, the olive family
How to recognize green ash. Ashes (except for one maple with an identity crisis and the invasive Amur cork tree) are our only trees with opposite pinnately compound leaves. The fruits of ashes, like those of maple, are single-seeded ones with a wing for wind dispersal; such a fruit is termed a “samara.” Unlike that of maple, which is double, an ash samara is single, thus resembling a little canoe paddle. (Now, where can I find a little canoe?)
Many ash species have a color as part of their common name. There’s white ash, green ash, red ash, blue ash, and black ash. They can be hard to identify, Green ash leaves have stalked leaflets, leaves that are green, not whitish beneath, and samaras that are narrower than the les frequently encountered blue ash.
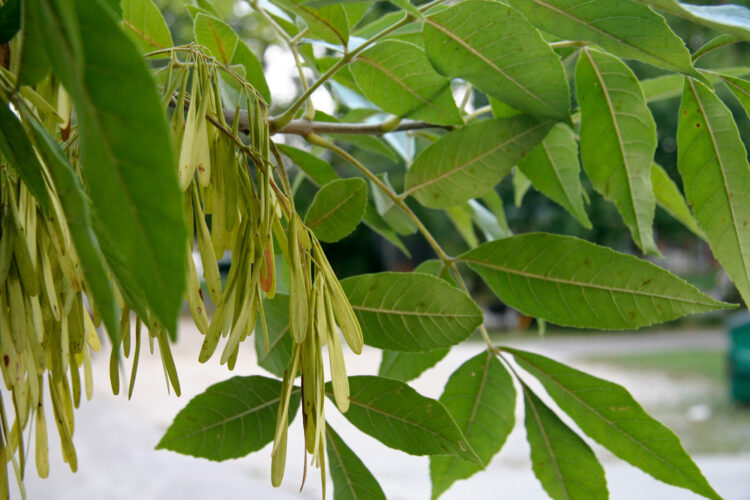

Green ash with samaras. Sept 7, 2007.
Flowers and fruits. Like all our other ashes except one (blue ash), green ash is dioecious (consisting of separate male and female individuals). Petal-less, male flowers consist of stamens that produce abundant wind-dispersed pollen.
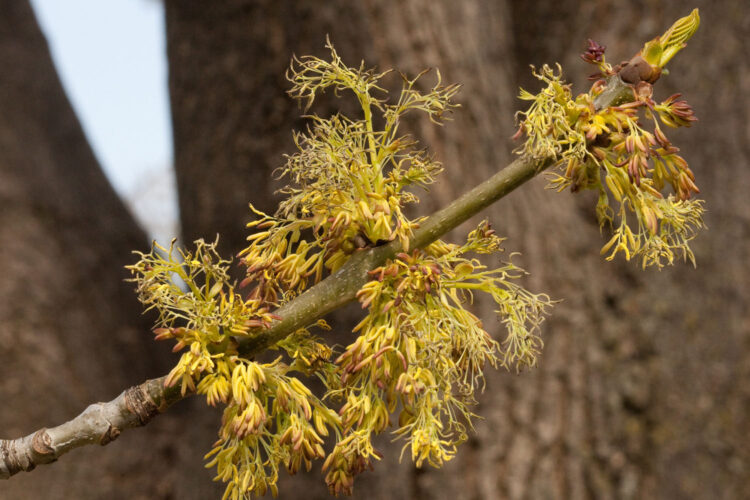

Male green ash flowers. April 10, 2010, Franklin County, Ohio.
Female flowers are little more than pistils with somewhat expanded pollen-receptive stigmas.
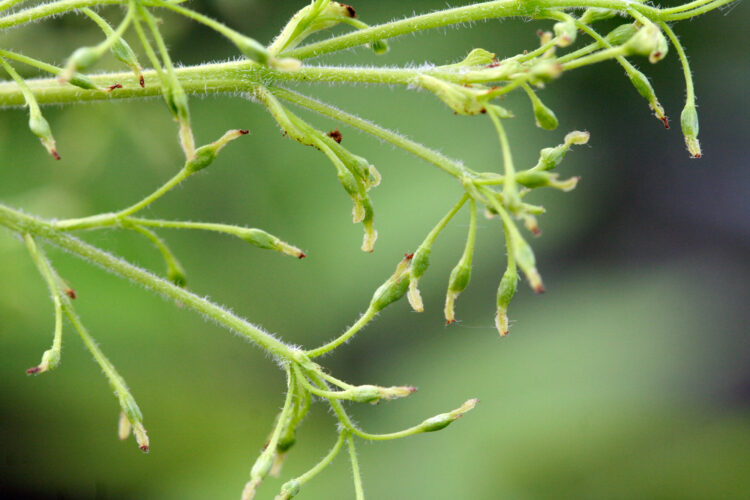

Ash female flowers. May 10, 2007, Franklin County, Ohio.
The fruits of green ash are lance-shaped pointed flat samaras–one-seeded dry fruits that are wind-dispersed.
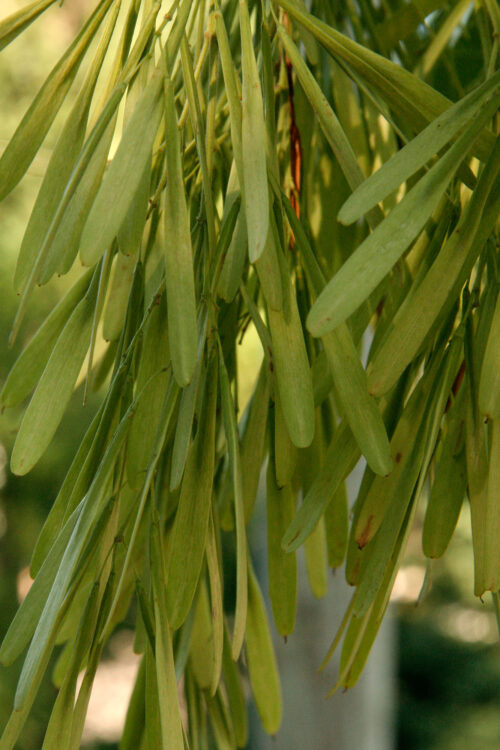

Green ash fruits are one-seeded winged samaras.
In the winter. Ash twigs have a true terminal bud, an oppositely arranged leaf scars that are more or less circular in outline, not reaching across the twig to touch as do those of maples. Green ash is best differentiated from the very similar white ash by the shape of the leaf scar–flat across the top as opposed to smiley-faced in white ash.
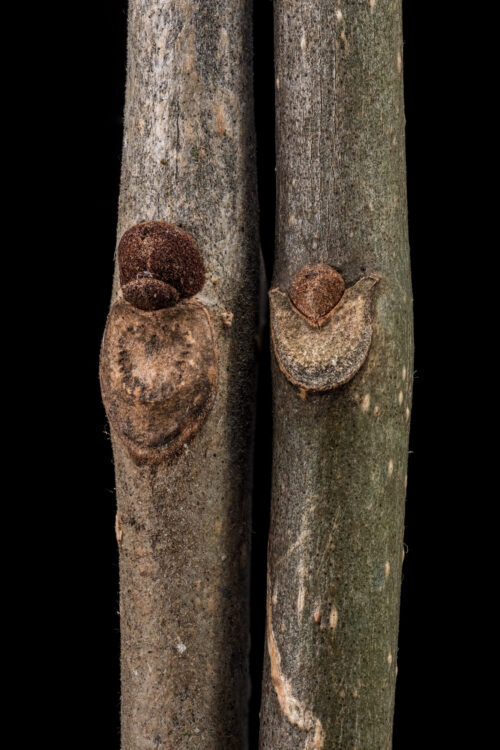

Ash times two. Left: green ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica)
Right: white ash (F. americana)
Where to find green ash. E. Lucy Braun, in The Woody Plants of Ohio (1961, 1989; The Ohio State University Press) tells us that green ash is “Wider ranging than any other ash, extending northward to eastern Alberta and Montana. A streamside tree. Common and widespread along streams in Ohio, where it is associated with white elm, silver maple cottonwood, and streamside willows.”
Scanned Image from an Old Book
(Flora of West Virginia, by P.D. Strausbaugh and Earl L. Core
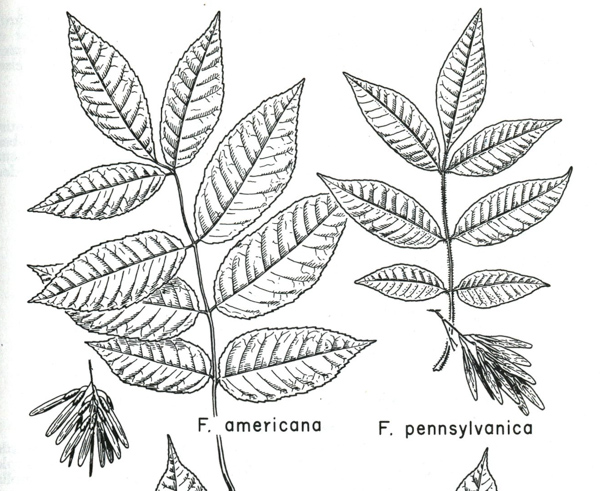
Green ash is on the right.
Oooh ooh. I have a question!
There seems to be a lots of dead and dying ash trees lately. What’s up with that?
Ash trees are severely threatened by recently introduced Asian wood-boring beetle, the emerald ash borer. It’s killing all types of ash trees as it spreads across the mid-west and northeastern U.S. In some places, transporting firewood across county or state border is prohibited. Research is underway to determine if there are any natural enemies of the emerald ash borer that could be used to help control it.

